Understanding VATS Lung Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
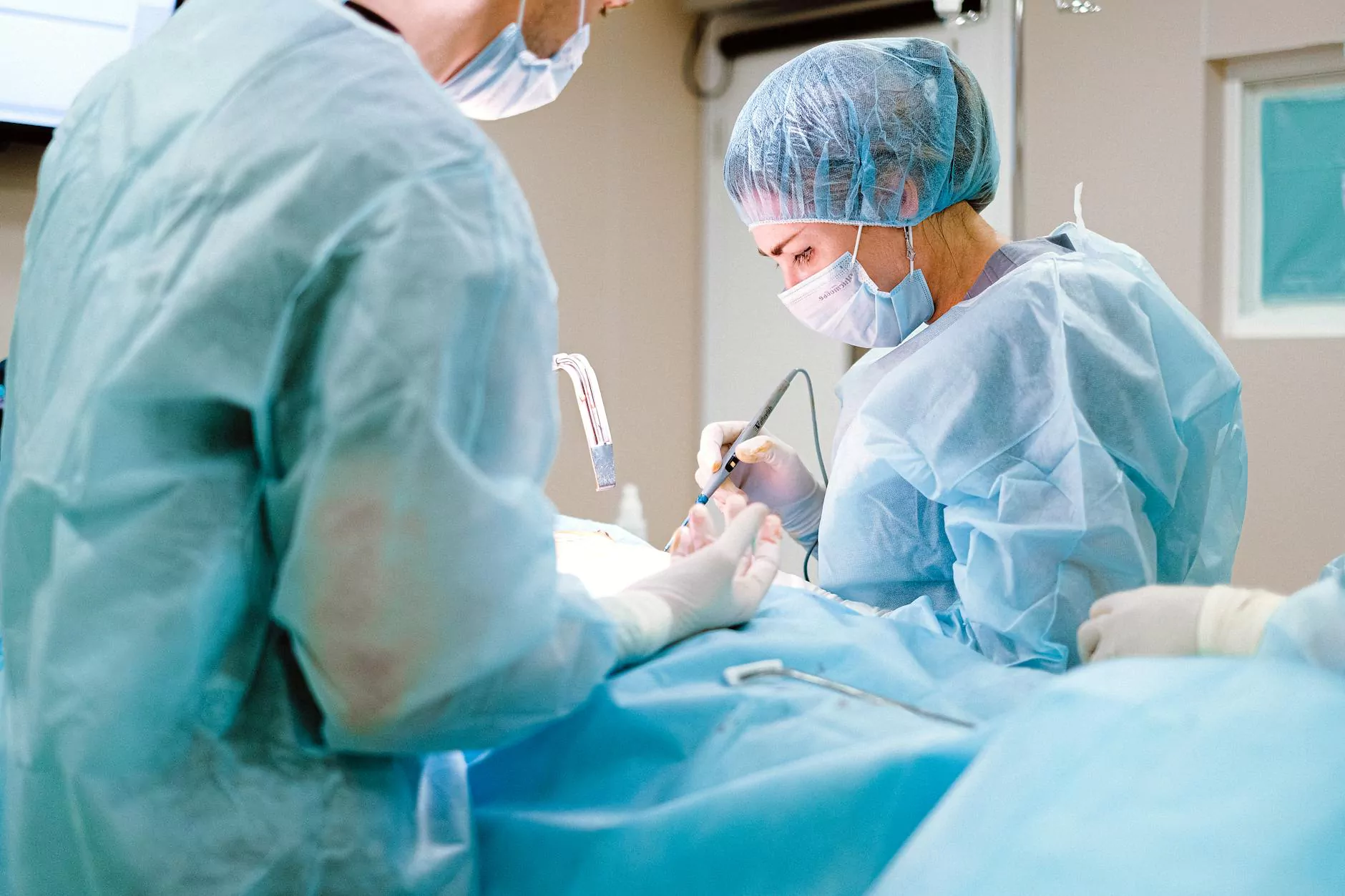
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the realm of lung surgery, offering patients a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods. With its ability to enhance recovery times, reduce pain, and minimize scarring, VATS is becoming increasingly prominent in hospitals and medical centers globally, including renowned institutions such as Neumark Surgery.
What is VATS Lung Surgery?
VATS lung surgery is a specialized thoracic surgical technique that utilizes small incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon during the procedure. Unlike conventional thoracotomy, which requires a large incision in the chest, VATS can be performed through several smaller incisions, generally ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 inches in length. This approach significantly reduces trauma to the body and optimizes the patient’s recovery process.
Indications for VATS Lung Surgery
VATS is indicated for various thoracic conditions, including but not limited to:
- Lung Cancer: For biopsies and resections of tumors.
- Pleural Effusions: Management of fluid build-up in the pleural space.
- Interstitial Lung Disease: Assessment and treatment of lung fibrosis.
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Releasing compression on blood vessels and nerves.
- Congenital Lung Malformations: Surgical correction of developmental issues.
The VATS Procedure: Step by Step
The success of VATS lung surgery is primarily attributed to the meticulous care taken during each phase of the procedure. The following is a detailed walkthrough:
1. Preoperative Care
Before surgery, patients undergo a thorough evaluation, including physical examinations, imaging studies (like CT scans), and pulmonary function tests. These assessments help determine the patient's overall health and suitability for VATS.
2. Anesthesia
General anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient remains unconscious and pain-free throughout the procedure. An anesthesiologist closely monitors vital signs.
3. Incision and Port Placement
Surgeons typically make three to four small incisions in the chest wall, referred to as "ports." These ports allow for the insertion of trocars and instruments.
4. Visualization and Procedure Execution
A thoracoscope (a small camera) is inserted through one of the ports, providing real-time images of the thoracic cavity. This visualization allows skilled surgeons to execute procedures such as:
- Biopsy: Collecting tissue samples.
- Lobectomy: Removal of a lobe of the lung.
- Wedge Resection: Removing small sections of the lung.
- Decortication: Removing a fibrous layer surrounding the lung.
5. Closure and Recovery
After the completion of the surgical procedures, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed either with sutures or surgical adhesive. Patients are then moved to the recovery room for monitoring as the effects of anesthesia wear off.
The Benefits of VATS Lung Surgery
The distinct advantages of VATS lung surgery make it an appealing option for both patients and surgeons:
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions lead to less pain and scarring.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Patients generally experience faster recovery compared to conventional methods.
- Reduced Hospital Stay: Many patients can go home within a few days post-surgery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: The minimally invasive nature of VATS correlates with fewer postoperative complications.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, there are important considerations to keep in mind when contemplating VATS:
1. Surgeon Experience
The success of VATS greatly depends on the surgeon's expertise and familiarity with the technique. It is crucial to choose a qualified thoracic surgeon with extensive experience in VATS procedures.
2. Patient Selection
Not every patient is a suitable candidate for VATS. Factors such as the complexity of the condition, the patient's overall health, and imaging findings could necessitate alternative surgical approaches.
3. Potential Risks
Even with its advantages, VATS may carry risks, including:
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
- Bleeding in the chest cavity
- Infection
- Persistent pain
Postoperative Care After VATS
Postoperative care is crucial for recovery. Following your VATS lung surgery, here’s what you can expect:
1. Pain Management
Patients experience pain post-surgery, which can vary in intensity. A multimodal approach, including narcotics and non-narcotics, will likely be implemented to manage pain effectively.
2. Respiratory Care
Deep breathing exercises and physiotherapy may be recommended to prevent complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis (collapse of lung tissue).
3. Follow-up Appointments
Routine follow-up visits are essential for monitoring recovery progress, assessing lung function, and ensuring that no complications arise in the post-surgical period.
Conclusion: The Future of Lung Surgery with VATS
In an era where advancements in technology and medical techniques have redefined patient care, VATS lung surgery stands out as a beacon of minimally invasive innovation. Its ability to improve outcomes, enhance quality of life, and streamline recovery processes makes it a preferred choice for numerous lung conditions.
As more healthcare professionals embrace this sophisticated technique, institutions like Neumark Surgery remain at the forefront of providing cutting-edge healthcare solutions. If you or a loved one is considering lung surgery, discussing VATS lung surgery with a qualified thoracic surgeon could be a pivotal step towards a healthier future.
© 2023 Neumark Surgery. All rights reserved.